
Power Factor Fundamentals
What we will learn:
- Most Industrial loads require both Real power and Reactive power to produce useful work
- You pay for BOTH types of power
- Capacitors can supply the REACTIVE power thus the utility doesn’t need to
- Capacitors save you money!
Why Apply PFC’s?
Power Factor Correction Saves Money!
- Reduces Power Bills
- Reduces I2R losses in conductors
- Reduces loading on transformers
- Improves voltage drop
What is PF ?
Introduction:
- Most plant loads are Inductive and require a magnetic field to operate:
- Motors
- Transformers
- Florescent lighting
- The magnetic field is necessary, but produces no useful work
- The utility must supply the power to produce the magnetic field and the power to produce the useful work: You pay for all of it!
- These two types of current are the ACTIVE and REACTIVE components
The Basics:
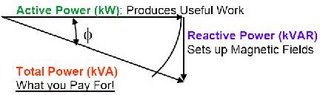
The Power Triangle:
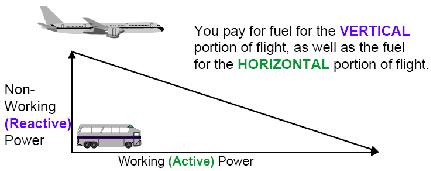
Similarly, motors require REACTIVE power to set up the magnetic field while the ACTIVE power produces the useful work (shaft horsepower). Total Power is the vector sum of the two & represents what you pay for:
Power Factor is the ratio of Active Power to Total Power:
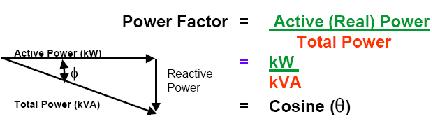
Power Factor is a measure of efficiency (Output/Input)
Why do we Install Capacitors?
Capacitors supply, for free, the reactive energy required by inductive loads.
- You only have to pay for the capacitor !
- Since the utility doesn’t supply it (kVAR), you don’t pay for it!
- Released system capacity:
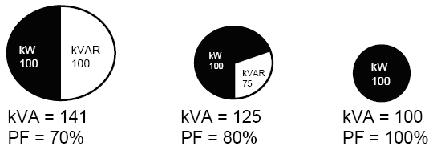
Decreasing size of conductors required to carry the same 100kW load at P.F. ranging from 70% to 100%
- Reduced Power Losses:
- As current flows through conductors, the conductors heat. This heating is power loss.
- Power loss is proportional to current squared (P Loss=I2R)
- Current is proportional to P.F.
- Conductor loss can account for as much as 2-5% of total load.
Capacitors can reduce losses by 1-2% of the total load
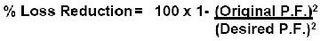 3. Voltage Improvement:
3. Voltage Improvement:- When capacitors are added, voltage will increase
- Typically only a few percent
- Not a significant economic or system benefit
Severe over-correction (P.F.>1) will cause a voltage rise that can damage insulation & equipment; or result in utility surcharges!
- Usually a result of large fixed capacitors at mains

Summary of Benefits:
Reduced Power Costs:
- Since Capacitors supply reactive power, you don’t pay the utility for it
- You can calculate the savings
Off-load transformers
- Defer buying a larger transformer when adding loads
Reduce voltage drop at loads
- Only if capacitors are applied at loads
- (minimal benefit at best)

No comments:
Post a Comment